The FDA (U.S Food & Drug Administration) approved the pill in 1960 which gave women safe access to contraceptives for family planning and beyond. As of 2020, the World Health Organisation (WHO) shared that 842 million women are using contraceptive methods, and to this day, we’ve seen four generations of birth control.
We know how difficult it is to choose the right contraceptive – been there, tried that. What if you need a pill that works to prevent pregnancy and regulate periods? What about the side effects, do some pills have higher/lower symptoms than others?
Everyone has questions before and even after starting the pill, and we’re here to answer some of them. Let’s start.
A brief history on birth control
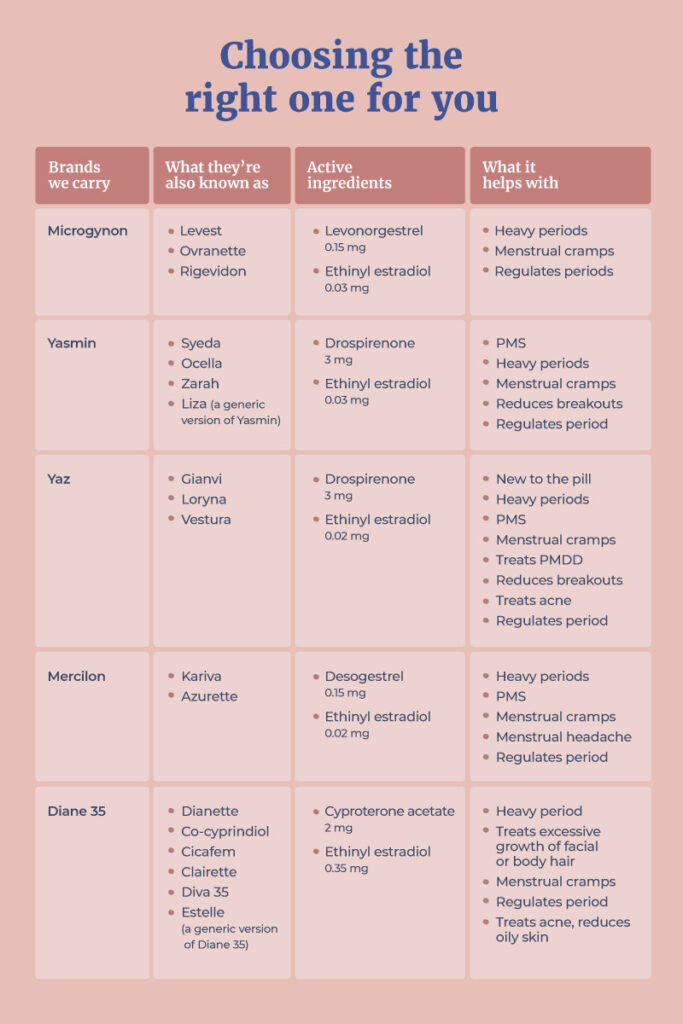
First-generation contained progestin norethindrone or norethynodrel. These are no longer in general use.
Second-generation contains progestin levonorgestrel (Microgynon 30), and are typically considered to be safe as they’ve been around since the 1970s.
Third generation pills contain the progestin desogestrel (Mercilon), cyproterone acetate (Diane 35/Estelle). Combined hormonal contraception can also be used in the form of a skin patch, like Evra.
Fourth-generation pills contain new progesterone drospirenone (Yasmin/Yaz)
Third and fourth generation pills have been developed to address androgenic side effects some people get when they use second-generation pills such as oily skin, breakout, female hair loss, weight gain.
How do birth control pills work?

Some contraceptives – like the pill, the patch, and the vaginal ring – contain small amounts of synthetic estrogen and progestin (aka progesterone). Let’s get to know two of our main sex hormones a little better:
Estrogen
Also known as oestrogen, estrone, estradiol, and estriol, it’s responsible for our physical features and the start of our menstrual cycle.
Progesterone
Produced in our ovaries every month, this hormone is important for our menstrual cycle and to prepare our uterus for pregnancy. What’s used in hormonal contraceptives is a synthetic version of progesterone, called progestin.
Why it’s included in contraceptives:
Progestin helps prevent pregnancy by suppressing ovulation and thickens the cervical mucus to block the sperm from reaching the egg. Estrogen helps control menstrual bleeding by giving it a ‘schedule’ and increases the potency of progestin.
How effective is the birth control pill?
With perfect use, the pill is 99% effective. However, because many people don’t use the pill perfectly (e.g. missing their pill), it can end up being 91% effective. Reminders, alarms, and sticking to a routine is important when taking the pill.
It’s normal to experience these side effects:
- Headaches
- Nausea
- Spotting (light bleeding between periods)
- Breast tenderness
- Changes in your periods (it might come early, late or stop altogether)
The good news is that the effects tend to subside in 2-3 months as your body adjusts to the hormones, and it doesn’t affect everyone either.
It does more than prevent pregnancy
It’s common for young women to be on contraceptives to treat acne or to regulate their menstrual cycle.
Depending on which brand, birth control can treat various concerns including hirsutism, acne, period cramps, endometriosis, heavy menstrual cycles, premenstrual syndrome or premenstrual dysphoric disorder (PMDD), to skip periods, or to reduce the risk of ovarian, endometrial and colorectal cancer.